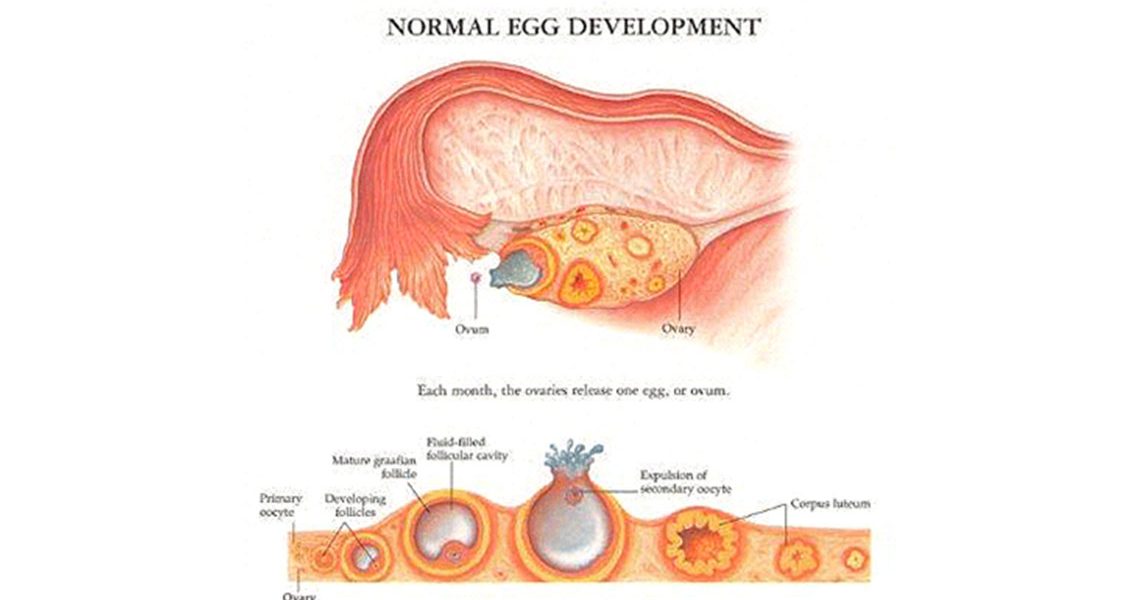
What is ovulation?
Usually each month one ovary will be stimulated by hormones produced in the brain. These cause a small cyst or follicle to grow on the ovary in which an egg develops. Another hormone then causes the follicle to release one egg to travel down the fallopian tube where it can be fertilized by the sperm which swims up from the vagina. This usually occurs around 14 days after the beginning of a period but can vary between 11 – 16 days.
What is ovulation induction?
Ovulation induction is a simple process which encourages the ovaries to release eggs, to maximize your chance of conception through intercourse or artificial insemination (IUI). It suits women who are producing low levels of hormones for ovulation, or who are not ovulating at all. Medication in the form of tablets or injections needs to be taken to stimulate hormones for egg production.
Who needs ovulation induction?
If a woman is not ovulating by herself then ovulation induction may be required.
The most common causes of failure to ovulate are
- Stress
- Weight fluctuations
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
Other causes may include disorders of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, and raised prolactin levels. In some cases, failure of ovulation is due to the ovarian failure. This may occur following treatment for cancer or maybe the start of the menopause – premature ovarian failure.
What is clomiphene citrate?
Clomiphene is a fertility drug that can increase the chance of ovulation occurring. It is an anti-estrogen and the most commonly used drug for inducing ovulation.
How should Clomiphene be taken?
Clomiphene is taken for 5 days early in the menstrual cycle – typically from day 2 to 6 of the cycle or day 3 to day 7. It is taken orally at the same time every day.
What are the potential side effects of clomiphene?
Bloating, pelvic pain, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, light-headedness, constipation, breast discomfort, fatigue and a change in menstrual flow can all occur while taking clomiphene. If you develop blurred or altered vision please discontinue clomiphene and contact the doctor.
What are the chances of conceiving with clomiphene?
For women whose only infertility problem is anovulation, up to 80% of patients will ovulate using this medication and 50% of those will conceive. Clomiphene may be combined with intrauterine insemination to boost the success of the medication by placing the sperm and egg in closer proximity to each other.
What are gonadotrophins?
Gonadotropins are fertility medications that contain FSH or LH alone or in combination. In contrast to clomiphene, which is given by mouth, gonadotropins are given by injections. A related medication is hCG, which is structurally similar to LH and mimics the natural LH surge. There are a variety of commercially available gonadotropin preparations.
How will the cycle be monitored while on ovulation induction drugs?
Ultrasound:
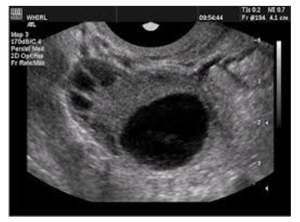 The doctor will often use one or more ultrasound scans to obtain an actual image of the ovaries and to regularly monitor follicle growth in the ovary beginning on or before day eight of the cycle, as follicles mature, they grow larger. Through ultrasound, the doctor will observe the effects of treatment on follicle growth and size, and decide when to give hCG injection (human chorionic gonadotrophin) to assist with the release of the egg.
The doctor will often use one or more ultrasound scans to obtain an actual image of the ovaries and to regularly monitor follicle growth in the ovary beginning on or before day eight of the cycle, as follicles mature, they grow larger. Through ultrasound, the doctor will observe the effects of treatment on follicle growth and size, and decide when to give hCG injection (human chorionic gonadotrophin) to assist with the release of the egg.
Blood tests:
Testing the blood every few days for oestrogen levels can monitor the response to treatment with FSH therapy.
Your progesterone level is usually checked six to eight days after you ovulate (about day 21 of a day 28 cycle). This is because progesterone levels rise following ovulation, peaking five to nine days after ovulation. This is known as your luteal phase. After the midluteal period, your serum progesterone levels will begin to fall if the egg is not fertilized.
What are the side effects of gonadotropins?
There are potential risks and complications associated with the use of gonadotropins. Side effects should be discussed prior to taking these medications. Despite intensive monitoring, up to 30% of gonadotropin-stimulated pregnancies are multiple. Of the multiple pregnancies, about two-thirds are twins and one-third are triplets or more. Premature delivery is a known risk for multiple pregnancies. The greater the number of fetuses in the uterus, the greater the risk of premature delivery. Premature delivery can subject the newborn to complications such as severe respiratory distress, intracranial hemorrhage, infection, cerebral palsy, and death. Some patients pregnant with triplets or more choose to undergo a procedure known as multifetal pregnancy reduction in an effort to decrease these risks.
In addition to problems associated with high order multiple gestations, another serious side effect of gonadotropin therapy is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), in which the ovaries become swollen and painful. In severe cases, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity and chest. In about 2% of gonadotropin cycles, hyperstimulation may be severe enough to require hospitalization. Careful monitoring of ovulation induction cycles with the use of ultrasound and/or measurement of serum estradiol levels, in conjunction with adjustment of gonadotropin dosage, will enable the physician to identify risk factors and prevent most cases of severe OHSS. When serum estradiol levels are rapidly rising and/or too high, or an excessive number of ovarian follicles develop, one method of best prevention is to withhold further gonadotropin stimulation and delay hCG administration until estradiol levels plateau or decline. Alternately, hCG can be withheld so that ovulation fails to occur, thereby lessening the severity of OHSS.
When should I test for pregnancy?
Most menstrual cycles are approximately 28 days long and ovulation occurs 14 days prior to the onset of menstrual flow. If you are pregnant the menstrual flow will not come. Test for pregnancy using a home pregnancy test 28-30 days after your last menstrual period.
If your period does not come, continue to test for pregnancy every second day. Contact the best doctors if your menstrual period does not come 35 days after your last period and the pregnancy test remains negative. Please also contact your doctor if you become pregnant! Please remember you may not conceive during the first cycle. Indeed, most patients require a few months of clomiphene treatment and sometimes dosage adjustments are required.
Reference:
Ovulation Problems and Infertility: Treatment of ovulation problems with Clomid and other fertility drugs Advanced Fertility Center of Chicago. Gurnee & Crystal Lake, Illinois